Maximise 2025 Tax Reliefs and Allowances for Business Growth
Chris Barnard • January 7, 2025
Maximise 2025 Tax Reliefs and Allowances for Business Growth
As 2025 unfolds, businesses across the UK are gearing up to capitalise on a range of new tax reliefs and allowances introduced in recent years. Designed to not just ease the tax burden but also to spur growth and investment, understanding and leveraging these incentives can transform your company’s financial health and set the stage for substantial growth.
In this guide, we will explore six key methods to help you get the most from these opportunities: the Annual Investment Allowance (AIA), Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credits, Employment Allowance, Tax-Free Staff Benefits, Patent Box Tax Relief, and the Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme (SEIS). Each of these areas offers unique advantages that can significantly impact your business strategy and bottom line.
Understanding Six Key Tax Reliefs and Allowances
1) Annual Investment Allowance (AIA) Increase
The Annual Investment Allowance (AIA) offers a fantastic tax relief opportunity for UK businesses, allowing them to deduct the full value of qualifying new equipment and machinery from their taxable profits in the year of purchase. This measure will permanently increase the limit of the annual investment allowance (AIA) from £200,000 to £1,000,000 for qualifying expenditure on plant and machinery incurred from 1 April 2023. This immediate tax deduction can significantly reduce your tax liability right away, unlike other tax reliefs which spread out over several years. By capitalising on this allowance companies can effectively decrease their tax liabilities while strategically reinvesting in their growth and efficiency.
At Collective Concepts Accounting, we see the AIA as a proactive incentive by the government, designed to spur investment by SMEs in the tools and technology they need to expand and thrive. The idea is simple: by investing in your business's growth, you're not only positioning yourself for success but also contributing to broader economic growth and job creation. This aligns perfectly with our mission to support your business growth through strategic financial planning and savvy tax advice.
To get the most out of the Annual Investment Allowance (AIA), it's essential to grasp which assets qualify, and the timing of purchasing new assets. AIA provides businesses with the opportunity to deduct the entire value of qualifying new business assets from their profits before taxes, promoting immediate tax savings and encouraging further capital investment. For an asset to qualify under AIA, it must be used for business purposes and be a tangible asset. This means the asset must have physical substance and can include items such as machinery, office equipment, and vehicles. Unlike tangible assets, intangible assets, such as patents, software, or copyrights, do not qualify for AIA. Understanding the distinction between tangible and intangible assets is crucial for businesses planning to make the most of AIA benefits.
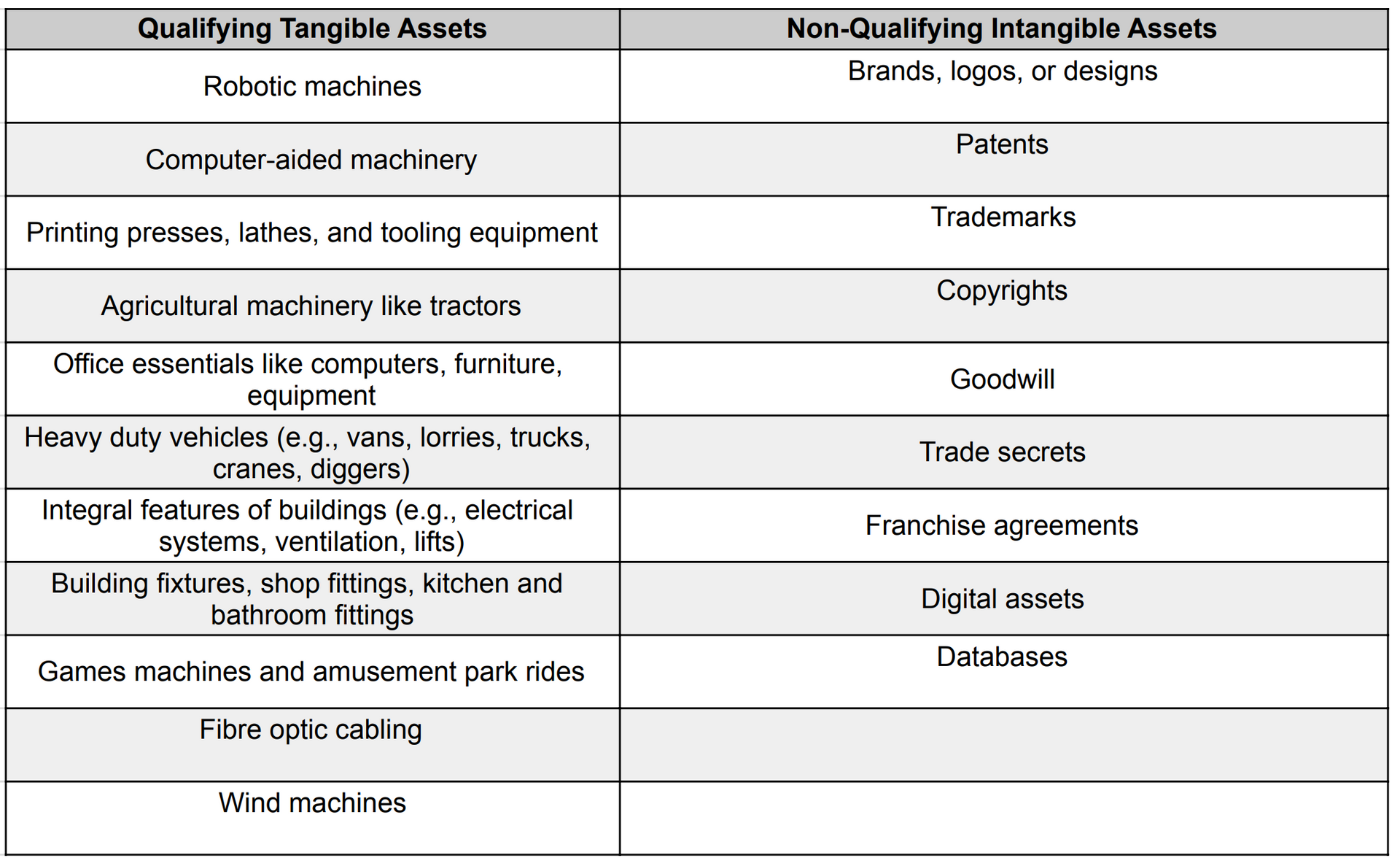
Additional Exclusions:
- Expenditure on assets used only for business entertainment purposes does not qualify.
- Assets acquired in the final accounting period of a business before it ceases trading are excluded.
It's important to ensure that assets are new and used solely for business purposes to qualify for AIA. Timing is also critical, as the AIA claim must be made in the tax year that the asset is purchased. This strategic approach to asset investment can significantly impact your business’s cash flow and overall financial planning.
If you're planning to invest in assets and want to ensure you maximise your AIA benefits, timing is key. If, for example, your business year end is 31st March you’d need to have receipt of the goods before the year end in order to be able to claim AIA within that accounting year. If the tax rate is going down your business will want to buy goods earlier in the year. Similarly, if the tax rate is rising, buying goods later in the year will help maximising those AIA benefits.
2) Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credits
Research and Development (R&D) Tax Credits have been instrumental in promoting innovation among UK businesses since their introduction in 2000. Targeted initially at SMEs, the scheme has expanded to include large companies through the R&D Expenditure Credit (RDEC). Significant upcoming changes will further refine how businesses can harness these incentives.
Overview of R&D Tax Credits
Purpose and Impact: R&D tax credits are designed to support companies that invest in developing new or enhanced products, processes, or services. This support is crucial for SMEs, covering a broad range of costs such as employee wages, raw materials, and certain overheads related to R&D activities. These credits help mitigate the financial risks associated with innovation and encourage continuous investment in R&D, helping businesses remain competitive and forward-thinking.
The purpose of Research and Development (R&D) is fundamentally to advance science or technology within a specific field by addressing and resolving scientific or technological uncertainties that cannot be easily determined by professionals using existing knowledge. The activities that qualify for R&D tax credits must be targeted efforts that directly contribute to this purpose, including both direct project work and certain indirect activities that support the core objectives. However, routine analysis, minor adaptations, or mere enhancements do not qualify. The projects must aim to significantly enhance knowledge or capabilities, either through tangible outcomes like improved products or intangible results such as increased efficiency. This scientific uncertainty, where outcomes are not predictable, is crucial for defining the scope and eligibility for R&D activities, underscoring the scheme’s intent to stimulate genuine innovation and problem-solving.
Recent updates to the administrative requirements for R&D tax claims have introduced new forms that companies must submit to streamline the process and ensure compliance. From 8 August 2023, an Additional Information Form is required for all new R&D claims. This form must be included with the submission of the CT600 tax form, ensuring that detailed and specific information accompanies the tax filings. Additionally, starting from accounting periods after 1 April 2023, a Claim Notification Form must be filed within six months of the accounting period's end. However, there is an exemption for companies that have made R&D claims in any of the previous three years, simplifying ongoing compliance for regular claimants. These changes are part of broader efforts to enhance the administration of R&D tax incentives and ensure that claims are substantiated and accurate.
Merging of R&D Schemes
From 1 April 2024, the RDEC and SME schemes will combine into a single scheme, offering a 20% taxable credit on qualifying expenditures. The actual relief received will depend on the corporation tax rate:
- At a 19% tax rate, the effective relief is 16.2%.
- At a 25% tax rate, it's 15%.
- At a 26.5% marginal rate, it's 14.7%.
Support for Research-Intensive SMEs
A dedicated SME scheme will continue for companies spending at least 30% of their total expenditure on R&D. These businesses will benefit from enhanced deductions and credits, with relief for losses up to 27% of qualifying spend. A grace period allows for temporary dips below the 30% threshold.
Focus on Domestic and Subcontracted R&D
Starting April 2024, R&D activities must primarily occur within the UK, though some overseas activities may qualify under specific conditions. Subcontracted R&D costs are capped at 65%, with eligibility dependent on the initiating party of the R&D work.
Preparing for Changes
With these updates representing a significant shift in accessing and applying R&D tax relief, businesses should reevaluate their strategies to maximise benefits. Ensuring compliance with new requirements while seizing opportunities for increased support is crucial.
3) Employment Allowance
The recent enhancements to the Employment Allowance are poised to significantly benefit employers, making it an opportune moment to consider how these changes can support your business's growth and staffing strategies.
Overview of Recent Changes to Employment Allowance
From 6 April 2025, the Employment Allowance has been increased, allowing businesses to claim up to £10,500, up from the previous £5,000. This substantial rise is designed to decrease the cost of employment, incentivising businesses to hire more staff and invest further in training and development. By reducing the financial burden associated with National Insurance contributions, this policy enhancement supports business expansion and workforce skill development across various sectors.
Changes to Class 1 National Insurance Contributions:
The threshold for Secondary Class 1 National Insurance contributions (NICs) will be reduced from £9,100 a year to £5,000 a year, starting from 6 April 2025 and lasting until 5 April 2028. This change means that employers will start incurring NICs at a lower earnings level, which aligns with the increased support provided by the higher Employment Allowance.
Additionally, the rate for secondary Class 1 NICs will rise from 13.8% to 15%. This increase is offset by the higher Employment Allowance, ensuring that more businesses can benefit, regardless of their size.
The recent reform also removes the previous restriction that barred employers with a secondary Class 1 NICs liability of over £100,000 in the preceding tax year from claiming the Employment Allowance. Now, all eligible businesses and charities can take advantage of this relief, elevating their ability to manage costs effectively.
How This Affects Your Business
These changes are designed to make employment more affordable and accessible, encouraging businesses to scale up their operations and contribute positively to broader economic growth. For businesses planning to expand their workforce or magnify employee benefits and training programs, the increased Employment Allowance provides a significant financial boost.
4) Tax Free Staff Benefits
Maximising tax reliefs and allowances extends beyond just financial operations. It also encompasses the valuable benefits you can provide to your staff tax-free. Offering these perks not only boosts morale but also enhances your team's overall productivity and job satisfaction without increasing their tax burden. Here are key tax-free staff benefits to consider:
Employer Pension Contributions: Contributions made by employers to registered pension schemes are tax-free and offer a compelling way to help employees plan for retirement.
Mobile Phones: Employers can provide employees with a mobile phone without any additional tax charge, even if the phone is used for personal calls.
Trivial Benefits:
Small benefits like occasional gifts or minor perks can be offered tax-free, provided they do not exceed £50 per benefit and are not given as a reward for services.
Health and Wellbeing Benefits:
Initiatives like annual health check-ups or providing eye tests and glasses for computer work can be exempt from tax.
Training and Development: Investing in your employees’ professional development through training courses directly related to their job is not only tax-free but fosters a more skilled workforce.
5) Patent Box Tax Relief
Patent Box Tax Relief is a significant incentive for companies engaging in innovative development, reducing Corporation Tax to just 10% on profits earned from patented inventions and certain other types of intellectual property. This scheme is designed to encourage companies to keep high-value patent management and development activities within the UK, thereby fostering a thriving environment for technological advancement and innovation.
By opting into the Patent Box, companies can substantially lower their tax liability on profits derived from their patented products or processes. This not only improves profitability but also enhances the return on investment in R&D and innovation. It’s particularly beneficial for businesses investing heavily in research and development, allowing them to align their tax strategies with business innovation efforts effectively.
Companies looking to maximise their 2025 tax reliefs and allowances should consider the Patent Box if they hold patents or are in the process of obtaining them. Engaging with this scheme can be a strategic move to significantly reduce tax costs while promoting sustained investment in innovation.
6) Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme (SEIS)
The Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme (SEIS) is a pivotal initiative designed to bolster investment in early-stage businesses in the UK. By offering up to 50% income tax relief on investments up to £100,000 per investor per year, SEIS not only incentivises individual investment into startups but also significantly reduces the financial risk associated with such ventures. This scheme is crucial for startups seeking essential capital to ignite growth and innovation.
Beyond the attractive tax relief, investors can also benefit from capital gains tax exemption on any gains realised from SEIS shares held for at least three years. Additionally, should the investment result in a loss, investors can elect to offset this loss against their capital gains or income tax, providing a further financial buffer.
For startups, SEIS is an invaluable tool for attracting investment. It enables them to raise up to £150,000 in total, which can be pivotal during the formative stages of their business when funding can be a significant barrier to growth and development. Companies looking to leverage SEIS must meet certain conditions, such as being less than two years old and having assets of no more than £200,000.
By facilitating easier access to investment, SEIS not only helps sustain the UK’s innovative startup ecosystem but also encourages a culture of entrepreneurship and growth. For investors, the scheme offers a substantial incentive to support new ventures with a reduced tax liability, fostering an environment where both businesses and investors can thrive.
Conclusion
As we navigate the complexities of the 2025 tax landscape, the opportunities for enhancing business growth through strategic tax reliefs and allowances are profound. The measures discussed, including the Annual Investment Allowance (AIA), R&D Tax Credits, Employment Allowance, Tax-Free Staff Benefits, Patent Box Tax Relief, and the Seed Enterprise Investment Scheme (SEIS), each offer unique avenues to reduce tax liabilities while promoting significant business advancement.
Leveraging these tax incentives correctly can not only lead to substantial financial savings but also drive innovation, enhance employee satisfaction, and attract crucial investment. Particularly, the expanded scope of schemes like AIA and R&D Tax Credits underscore a clear governmental intent to support businesses in their growth and innovative projects.
It's crucial for business leaders to stay informed and proactive, ensuring that they align their tax planning with these beneficial schemes. At Collective Concepts Accounting, we are committed to guiding you through these opportunities, helping to maximise the benefits and positioning your business for success in an increasingly competitive environment. Let's harness these tax reliefs to build a resilient and thriving business landscape for 2025 and beyond.
Book a chat with us today to see how we can help you leverage the tax reliefs and allowances and accelerate your business’s growth in 2025.
Related Posts


© 2023 All Rights Reserved Collective Concepts Accounting Ltd. Registered office is Sussex Innovation Centre, Science Park Square, Brighton, BN1 9SB. Company Registration Number 14158965












